Common Pharmaceutical Lab Mistakes & How to Avoid Them (GLP, RCA, Safety Guide)
Imagine it’s your first day in your pharmaceutical lab internship, and you’re so excited to start and make a productive difference in pharma. With your gloved hands, it’s time to measure the ingredients for a new drug batch. Are you confident in doing it right? Imagine the label on the chemical is misread by you, or you have forgotten a data entry to be made. After a few days, your supervisor informs you that the batch has failed and the company you’re working for is facing a huge loss. Now this mistake tells us that even a small mistake in a small pharmaceutical lab will lead to failed batches in drug discovery and will result in dangerous medicine for the public, and finally, it leads to intense regulatory investigation. Have you ever imagined if you could skip a single step, it would turn your hard work into a disaster? Do you ever think some common practices, such as proper documentation, carefully handling samples and following good laboratory practices(GLP), would have prevented you from this error? Let me tell you something very important. In the pharmaceutical industry, the most important thing is accuracy more than the target. Any drug batch you do should strictly follow the safety and quality standards because people’s life is involved in this. The mistakes you make not only impact cost, money and time, but they also put the patients at risk where they cannot undergo any treatment. This is the reason labs use systems for error prevention from GLP and Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to maintain proper safety protocols.
This article will provide you proper understanding and how to avoid the most common lab mistakes we students make. You will not only know where you have gone wrong but why these mistakes happen and how the high-tech tools, such as GLP, root cause analysis, and good safety practices, help you stay confident and free from making mistakes. You will also learn the prevention strategies and will feel ready for your next experiment. Are you ready to know the secrets behind safe, accurate and successful pharmaceutical lab work? Come, let’s know the real secrets.
Introduction for Good Laboratory Practice, RCA, and strong safety
The work we do in the lab should be more accurate because it’s not just like a technical detail; it stands as the main pillar in drug safety, quality and regulatory compliance. Mistakes and the laboratory error we make in the lab will lead to major problems where a single error can lead to the destruction of the entire batch of drug, introduce safety risks, cause harm to the patient and also lead to expensive regulatory actions. For students like us, it is important to understand the common mistakes and the laboratory error we make in the lab, and we have tools which help us not to repeat our mistakes. Some of the tools include GLP (Good Laboratory Practice), RCA(Root Cause Analysis), and strong safety habits are the main steps to building a successful pharma career.
This article gives you a proper understanding of your mistakes in the pharmaceutical lab , why they matter for health safety and secrets to avoid them.
What is Good Laboratory Practice, RCA and Lab Safety?
What is GLP(Good Laboratory Practice)?
First, let’s understand what this GLP is. So GLP basically means guidelines, or we can say procedure to be followed, so they are the guidelines which have been set internationally to ensure that the testing process is done in a transparent, reliable and consistent manner. So the main GLP principles include well-documented SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures), qualified personnel, validated equipment for proper results, maintaining clear records and strictly adhering to safety and ethical practices of the drugs. In your learning era, that is in your academic journey, learning GLP will help you to be future-ready and reduce your confusion. The companies prioritize the candidates who are well-trained in GLP because they will know the common safety guidelines and how to work effectively and confidently.
What is RCA (Root Cause Analysis)?
This term is new to you but don’t worry let me make it simple and understanding so basically the term root tells us as it is something which is related to core so if there is a problem in the root of the plant do you think you’ll get a better yield no the plant dies in this case so root cause analysis is nothing but a systematic analysis to find the reason for our mistakes. This is not the type of analysis which will blame people directly without any reason, but instead it gives us a clear understanding of how and why the error happened. So this tool helps us to know the root cause of the problem and solve it without causing any problems. Many students and freshers perform superficial root cause analysis where they notice the results are failed, but they tend to forget the main reason for the failure the reasons such as wrong calibration and also unclear SOP wording. There are professional tools such as 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams, which make the process clear.
What are the Lab Safety Essentials we have to follow?
In the lab premises, the safety in pharma labs is important and cannot be left behind. Here are some of the key aspects which we have to keep in mind :
- PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
Our personal hygiene and care is the first important thing which has to be followed always wear lab coats don’t forget and never enter a lab without lab coat it will result it laboratory error, gloves is important to keep your hands protective against any chemical, masks are important to keep your lungs free from any harmful chemical gases and eye protection if in case your dealing with any chemical which may harm your eye so PPE requires to maintain Good Laboratory Practice
- Chemical Handling
The chemicals we use in our lab is harmful for both our skin and health which have to be handled with care first before using a chemical make sure you read the chemical hazards of the chemical, labelling of the chemical is important where improper labelling will lead to wrong chemical usage, storage of the chemical is very important where the chemical should be stored securely, the last and important precaution is the disposal process where the chemical bottles and solvents should be disposed properly.
- Biological Safety
This safety ensures the safety of our health against infections and microbes. While working in a biosafety lab, it is our responsibility to be safe against any viral infections caused by the microbes using a biosafety cabinet with safety precautions. For a safer workflow, sterilization is the main step to have a safe working environment is important if you have to follow Good Laboratory Practice
- Equipment Safety
To have a safe handling of machines, it is important to read the instructions first and follow them properly. Maintenance of the equipment is important so that the equipment functions properly and also ensures that safety precautions are taken to avoid accidents.
Common Pharmaceutical Lab Mistakes with Examples
- Documentation Errors
In the process of drug development the common mistake takes place during the documentation step where poor documentation will lead to wrong entries entered in the document and also your handwriting which should be easy for you to read and for anyone who sees your document also writing wrong units will lead to failures For example you are recording a incorrect pH value in your report this will lead to failure of the entire batch which will result in wastage and also regulatory investigation which helps in quality improvement.
- Poor Handling of Sample
While you’re working in the lab, the most important step is to keep yourself clean at least clean your hands, which you will be using for handling the samples because it will lead to cross contamination and labelling your samples this will confuse you and waste your time, the most important step is the storage which plays a major role in the growth of the organisms. For example, as we all know, bacteria are grown under an incubator, and fungi grow at room temperature both if placed in different temperatures, we won’t observe any growth.
- Incorrect Calibration & Instrument Errors
As I said earlier, proper usage of instruments and calibration accuracy are very important before using calibrations. We should have a proper update; we should not use expired calibration. And as we know in instruments, we have that warnings section where we need to check and follow the precautions. For example we give an inaccurate HPLC reading because of a missed calibration, it will lead to danger of the product’s launch if we don’t follow Good Laboratory Practice, which results in quality improvement
- SOP Deviations
This is one of the major problems we face, and do where we skip some of the steps which have to be followed, we have to not change the step and rearrange the steps, and also using outdated SOPs will result in failure of the experiment. For example, when we are doing the dissolution testing, there are certain steps to be followed; instead, if we skip or alter the steps, it will lead to wrong results and will also lead to regulatory action.
- Analytical Technique Errors
In the lab, we do analysis where we use pipettes for experiments where proper pipetting is very important for proper mixing, and the most important step is the reagent preparation, where reagents play a major role in the experiment, where proper checking of the composition is important and weighing the chemicals is important which is important for the proper procedure and output of the experiment. For example, you do wrong pipetting, and it leads to the failure of the experiment.
- Proper Understanding of Method
Before doing an experiment, make sure you read the procedures properly and understand the steps first, read the steps carefully and analyze them, and make sure you get all the required reagents for the step and grasp the critical steps. For example, we use a wrong filtration membrane without proper knowledge, then it will finally lead to sample loss and contamination.
- Poor Time and Workflow Management
Before working on an experiment, make sure you plan the work accordingly and do not rush with the steps, which will lead to quality improvement and overload of the instruments, which will result in errors and delay of work. For example, scheduling overlapping HPLC runs may result in bottlenecks, in sample mix-ups and also in instrument crashes.
- Safety Negligence
During our work in the lab, it is our responsibility to work with safety precautions and not take any risk during spills, and even mishandling of solvents will result in accidents. For example, we don’t wear gloves during an exothermic reaction, which will cause burns and also result in serious injury this results if there is no Good Laboratory Practice followed.
- Data Integrity Mistakes
When you’re working with data, and you want to note down the results, do not alter the results, which will result in wrong information. Instead of using scrap paper, use an official record, and do not violate ALCOA (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate) principles. These types of mistakes will lead to regulatory damage. Correction in this will result in quality improvement
How to Avoid These Mistakes
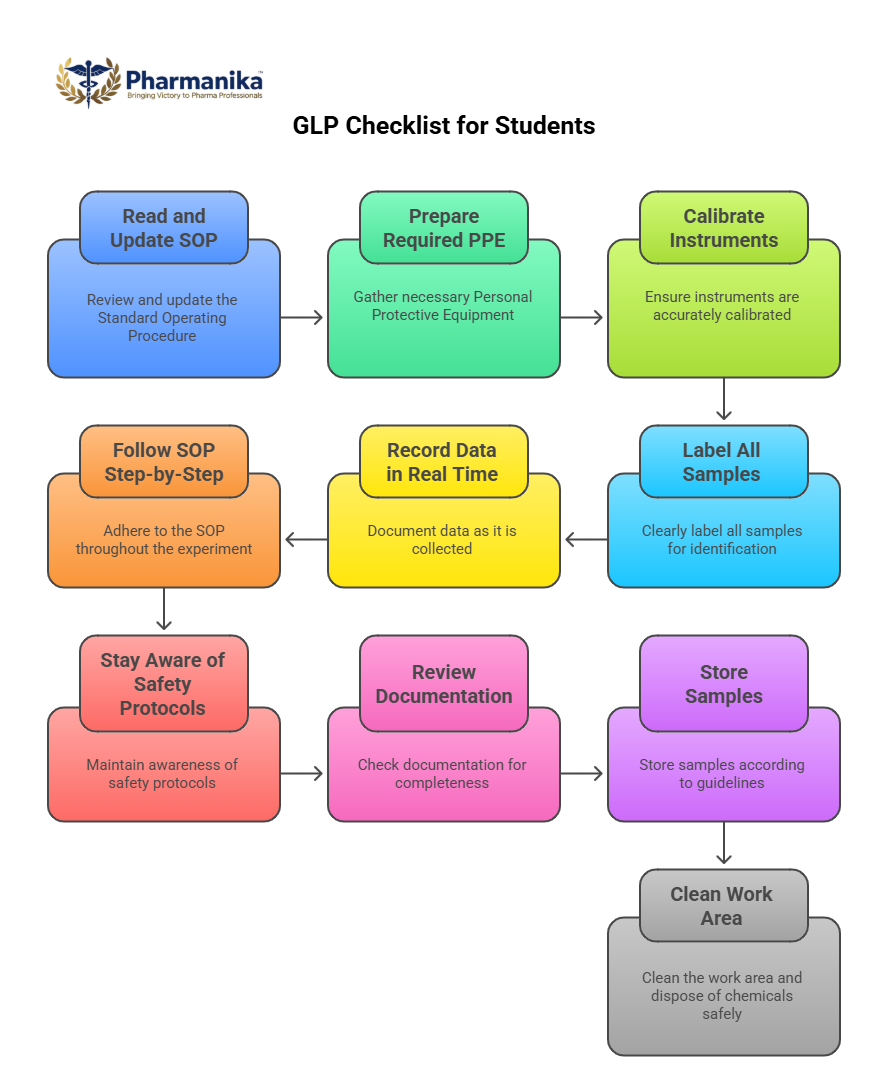
Good Laboratory Practice Checklist for Students
Before Starting
- Read and update the SOP
- Prepare required PPE
- Calibrate instruments
- Label all samples
During Experiment:
- Record data in real time
- Follow SOP step-by-step
- Stay aware of safety protocols
After Experiment:
- Review documentation for completeness
- Store samples according to guidelines
- Clean the work area and dispose of chemicals safely
Documentation Best Practices
Understand and apply ALCOA+ principles—everything must be:
- Attributable: Signed or initialed by who did it.
- Legible: Easy to read, not smudged.
- Contemporaneous: Written as the work happens.
- Original: Directly on official forms, not scrap paper.
- Accurate: Correct and factual.
Make proper and concise records. Please make sure to avoid scribbles, use only correct entries, do not update wrong entries and always double-check your units. Here are some of the digital records, such as ELN and LIMS, which are preferred in modern labs, but still the paper records are still common but as if we require both clarity and completeness.
Quick Revision Tables & Checklists
Common Errors vs. Solutions Table
| Error Type | Typical Example | Solution |
| Doc errors | Wrong units | Check before submit |
| Sample handling | Mislabeling | Label immediately |
| Calibration | Missed calibration | Daily logbook |
| SOP deviation | Skipped step | Read SOP fully |
| Technique error | Pipetting mistake | Practice, double-check |
| Safety negligence | Ignored PPE | PPE checklist before entry |
| Data integrity | Late entry | Write in real time |
Good Laboratory Practice Compliance Starter Checklist
- Read SOP for each test
- Wear correct PPE
- Calibrate all equipment
- Label samples before use
- Record data contemporaneously
- Use correct units/forms
- Double-check entries
- Review cleanup/disposal steps
- Store samples correctly
- Leave the workspace clean
Lab Safety Do’s & Don’ts
Chemical Labs
- Do: Use a fume hood, wear gloves
- Don’t: Mix unknown chemicals
Biological Labs
- Do: Autoclave waste, use biosafety cabinets
- Don’t: Mouth pipette biological samples
Analytical Labs
- Do: Calibrate, follow instrument SOPs
- Don’t: Overload the system with too many runs
Conclusion for mastering Good Laboratory Practice, root cause analysis, and strong safety
Mastering GLP, root cause analysis, and strong safety habits early is the key to becoming a reliable, industry-ready pharma professional. Students and freshers who take the time to work slowly, accurately, document every detail, and follow safety protocols not only avoid mistakes but set themselves up for long-term career success. Remember that in pharma labs, results and reputations are built on the foundation of careful, accountable, and safe work. Your commitment today will make you a trusted scientist tomorrow. Don’t rush—focus on accuracy, documentation, and safety with every experiment.




