Clinical vs Industry: The Battle Of Pharmacy Career Paths
Choosing a career path after completing your pharmacy degree is one of the most important decisions a graduate will have to make. For many years, the primary challenge for pharmaceutical graduates was limited to community retail for B-Pharm graduates or hospital clinical practice for Pharm-D graduates. However, career opportunities in Industrial Pharmacy have expanded. This is because the pharmaceutical sector has now evolved.
This guide will help you define the roadmap for the industry careers and clinical careers. It provides a deep understanding of the roles and responsibilities, skills required, rewards that you get from the respective roles, and the challenges of both the clinical and industrial pharmacy areas.
In addition, this article will not only provide information about the highly specialized fields of clinical research and advanced manufacturing. It will also help you to analyze how rapidly the pharmaceutical industry is growing. Furthermore, you will see how it is reshaping the demand for pharmacy career options globally.
Understanding the Modern Pharmacy Career Options
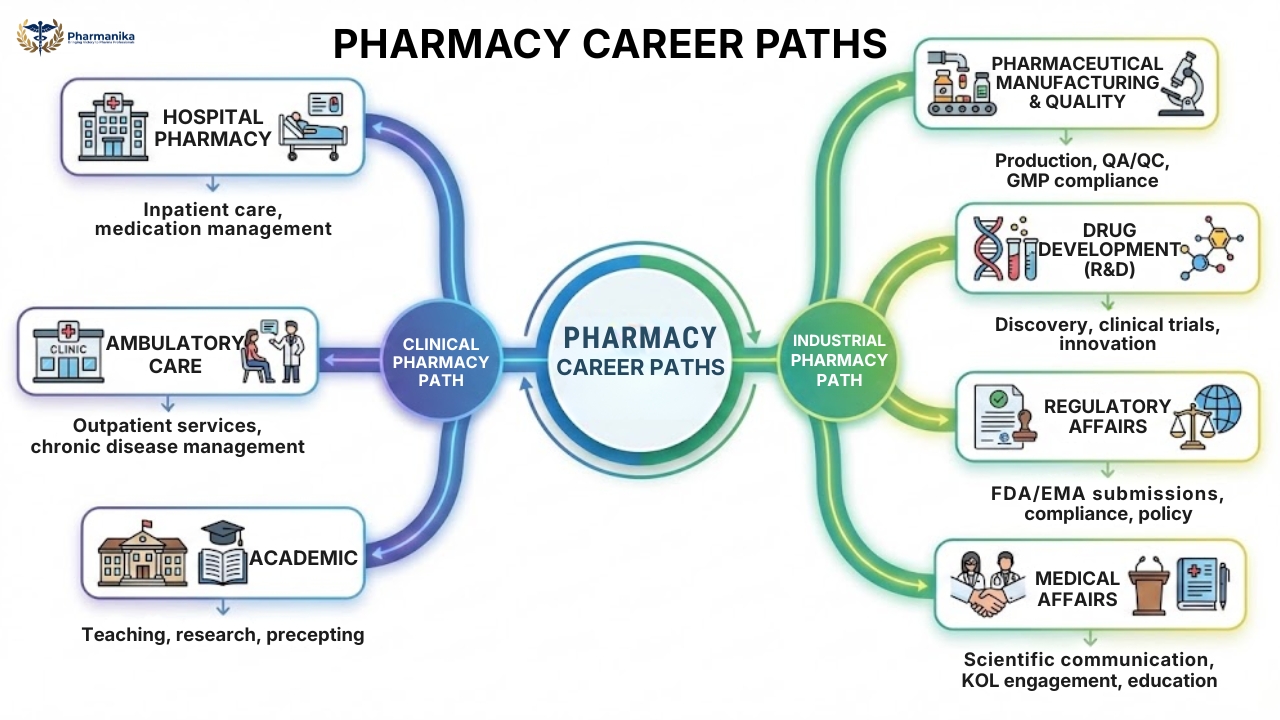
The pharmacy profession has evolved, and now it is involved in patient care, clinical research, and regulatory monitoring, etc. The core careers in the pharmacy are divided into two categories: that is clinical careers and industrial careers.
The clinical career path :
The clinical path involves direct interaction with the patients, physicians, and other healthcare providers in the hospital. These includes
- Hospital pharmacy
- Ambulatory care
- Academic
The industrial Pharmacy Career path
The industrial Pharmacy path deals with the drug from its discovery in the lab to its final delivery and post-market surveillance. These include:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Quality
- Drug Development ( R&D)
- Regulatory Affairs.
- Medical Affairs
Inside the Clinical Pharmacy Scope
The clinical pharmacist is one of the important members in the healthcare team; this role involves maintaining the therapeutic effectiveness and reducing the drug side effects. To become a clinical pharmacist, one should pursue a Pharm D, and some specialised certifications may also help to get a successful career in this path.
Hospital Pharmacy and Specialisation
Hospital Pharmacists are the experts in medication within inpatient hospitals. This role involves dispensing the medicines, assisting in the patient rounds, and also specialising in complex areas like the following:
- Infectious Disease: Optimizing antibiotic use to reduce the chances of resistance
- Critical care: Managing Rapid-Sequence Intubation, Vasoactive Drips, and Parenteral Nutrition in the ICU
- Oncology: Preparing harmful medications and managing chemotherapy regimens and toxicities.
Ambulatory Care
- Ambulatory care pharmacists work with outpatients and often under collaborative practice agreements (CPA).
- This role involves dosage adjusting, managing the drug therapies for chronic conditions like diabetes, heart failure, anticoagulation, etc.
- This role mainly involves improving patient adherence and outcomes, which represents the growth of direct patient pharmacy career options.
Clinical Research
- Clinical research is the scientific discovery of medicines; the pharmacist who specialises in this area should ensure the safety, accuracy, and ethical use of the investigational products.
- The pharmacist’s role in clinical research involves managing the complex protocols, ensuring drug accountability, and monitoring patient safety during clinical trials.
Role of the Pharmacist in Clinical Research:
Clinical Research Pharmacist (CRP) serves as the most important role in investigating drug integrity. The following are the responsibilities that are involved in the clinical research pharmacist role.
- Investigational Drug Services (IDS) Management: Setting up and managing the IDS pharmacy, which maintains all the trial medications in the house and dispenses them to the patients. It is important to make sure to adhere to blinding, randomisation, and accountability logs during the trials.
- Protocol Interpretation: Translating the research protocols in a way to dispense the medicines in IDS Pharmacy and administering the procedures for nurses and physicians.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all activities adhere to the Good Clinical Practice ( GCP) guidelines, FDA/ICH regulations, and institutional policies. The Clinical Research Pharmacist often participates in the site audits and inspections, too.
Key Skills and Requirements:
- Core skills required include: Detail-orientation, Regulatory knowledge ( GCP/ICH), strong communication skills, and organisation skills, which are required for maintaining the documentation and inventory.
- Education: Pharm D + Residency + Optional Clinical Research Fellowship or CCRC certification ( Certified Clinical Research Coordinator)
Salary and growth
- Salary (U.S.): Experienced CRPs can expect salaries ranging from approx 135,000 to 165,000 dollars per year; the salary differs by location, institution size ( academic vs. private), and experience level.
- Growth: due to the rise in biologics and personalized medicine, the clinical research career ensures a stable career, and there is also a growing demand for pharmacy experts.
Challenges in the Clinical Path :
- Regulatory Burden and Protocol Complexity: Getting approval from IRB is time-consuming, and the trials are complex, which target smaller and specific patient populations. CRPs have the responsibility to manage these regulatory and ethical restrictions.
- Staffing: Hospitals often involve long hours, rotating shifts like nights, weekends, and holidays, and have high patient volumes that significantly lead to restlessness.
- Administrative Tasks: A significant amount of the clinical pharmacists ‘ time will be consumed by administrative tasks, documentation, and managing authorisations.
Inside the Industrial Career Path
Industrial Pharmacy is the career path that involves drug discovery, drug distribution, and the combination of science, engineering, and business strategies.
The Stages Of Industrial Pharmacy ( Product Lifecycle)
The following are the roles in Industrial Pharmacy that make sure the drug reaches the patient in need.
Pharmaceutical Research and Development (R&D)
- R&D is the area where the new compounds are explored, tested, and transformed into useful dosage forms.
- Pharmacists in R&D use their deep understanding of drug chemistry, pharmacokinetics, and formulation science to design the final product.
- The Job roles that are involved in this area are as follows:
Formulation scientist
- Develops the optimal dosage forms like tablets, capsules, injectables, etc., that make sure that the drug is stable and bioavailable ( effectively absorbed by the body).
- Pre-Clinical Testing: This role involves working with the toxicologists and biologists to assess the safety and efficacy of new drugs before the human trials.
Manufacturing and Quality Assurance in Pharmacy
- This is the area that is responsible for scaling up production and making sure that the integrity of every batch.
- Quality Assurance (QA): Qa is a systematic process that ensures the product is designed and manufactured according to cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices) guidelines.
- QA creates and maintains the entire quality system in the manufacturing Plant.
- Skills: attention to detail, strong knowledge of cGMP, auditing skills, and proficiency in deviation management (CAPA- Corrective and Preventive Actions).
Quality control:
- QC analysts perform the chemical, physical, and microbiological tests on raw materials, in-process samples, and finished products to ensure that they meet the specifications.
Regulatory Affairs (RA)
This role requires the knowledge of drug mechanisms and regulatory statutes that a pharmacist will have.
- Core function: Preparing and submitting detailed New Drug Applications(NDAs) or Marketing Authorisation Applications (MAAs) to bodies like the FDA or EMA.
- Impact: RA Specialists determine the speed and success of the product market entry. They must constantly monitor the evolving global regulatory environment.
Salary and Work Culture in Industrial Pharmacy:
The industrial path offers some of the highest salaries. They are as follows
- Salary (U.S): Mid to senior-level industrial pharmacists (E.g., in Regulatory Affairs, Medical Affairs, or R&D Management) typically earn between 140,000 to 200,000 + annually, often supplemented by performance bonuses.
- Work culture: Generally, they have fixed daytime schedules like 9-5 or similar, with less weekend and holiday work than clinical roles. The focus is on the corporate objectives, project management, and cross-functional team collaboration.
Comparison between the clinical pathway and the Industry Career pathway
The choice between Clinical and industrial Pharmacy career options will depend on the personal preference for work environment, desired impact, and career path.
Salary Expectations and Financial Growth
- Entry level (U.S.): A new clinical pharmacist graduate and an entry-level industrial pharmacist, likea QA/QC Associate, are competitive, generally starting around 90,000 to 115000 dollars depending on the location.
- Mid-career: a specialist clinical pharmacist, such as in cardiology or oncology, may earn up to 150,000 dollars, but an industrial pharmacist ina regulatory affairs or medical science liaison (MSL) role can earn up to 160,000 to 200,000 dollars with yearly bonuses.
- Global Trends: In the emerging markets like India, Industrial roles, particularly in R&D and regulatory, often provide faster salary growth and higher compensation within MNCs compared to local clinical roles.
Required skills
Clinical career path Skills:
- Critical Thinking and Patient Assessment: Rapidly analysing patient lab data, diagnosis, and medication history to make immediate, life-saving decisions.
- Communication: clear professional communication with physicians and patient counselling.
- Empathy and resilience: Dealing directly with illness, ethical dilemmas, and emotionally challenging patient outcomes.
Industrial Path Skills:
- Regulatory interpretation: Deep knowledge of cGMP, cGLP, and regulatory filings (NDA/ANDA)
- Project and Process Management: Ability to manage complex projects with long timelines, cross-functional teams, and tight budgets.
- Data analysis and statistics: Necessary for R&D, clinical research data review, and quality trend analysis. The focus shifts from individual patient data to population-level or batch-level data.
The influence of the Pharma Industry Growth on career demand
The coming demand will see an exponential growth and transformation across the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors. Understanding where the market is expanding is important. You should consider this before making career choices in pharmacy career options.
Global Pharma Industry Growth
The global pharmaceutical market is about to reach approximately 2.35 trillion dollars by 2030. It is growing at a compound Annual Growth Rate(CAGR) of 6% over. This growth is due to the following reasons:
- Chronic diseases and Aging populations: As global populations age, chronic conditions like cardiovascular diseases, Diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders are increasing, which demand new and maintenance therapies.
- Technological innovations: advances in genomics, biologics, and cell/gene therapies require entirely new sets for manufacturing and distribution processes, which creates new specialised industrial Pharmacy jobs.
- The rise of AI and Personalized Medicine: Artificial intelligence is used in drug discovery and clinical trial designing, and manufacturing quality control, making it necessary for pharmacists with hybrid skills in data science and pharmacology.
How Growth Impacts Clinical Job Demand
Demand for Clinical Specialists
- The next generation of Oncology, immunotherapy, and rare disease treatments requires dedicated pharmacy specialists in the hospitals.
- Pharmacists are responsible for dosing, side effects reduction, and administration logistics of these drugs.
Decentralised Trials
- The shift towards Decentralised Clinical Research models (DCTs) using digital Tools and remote monitoring requires pharmacists who can manage investigational products and protocols outside of the traditional hospital settings, which leads to the opening of new roles.
How Growth Impacts Industrial Pharmacy Job Demand
Regulatory Affairs in a Globalised Market
- As companies are chasing the market share in regions like China, India, and Latin America, the regulatory affairs jobs are multiplying.
- Specialists in regulatory affairs who can interpret and reconcile the global standards that differ are essential.
- Furthermore, this area requires pharmacists who can manage the strategic and legal dimensions of the drug market and compliance globally.
The Quality Revolution:
- The volume and complexity of manufacturing biologics mean that traditional manual quality checks are insufficient.
- The demand for experts in quality assurance, pharmacy, and quality control is rising.
- Specifically, the industry needs pharmacists who can understand automated systems, data integrity, and computerised system validation (CSV).
Key Areas of Future Growth in industrial Pharmacy Career path:
Advanced Manufacturing and Supply Chain
This area involves optimizing production, ensuring the drug stability across the global temperatures, and managing the logistics.
Key Roles
- Supply chain Pharmacist, Validation specialist, Cold chain Logistics Manager.
Growth
- Pharma Industry Growth Relies on securing resilient supply chains, especially post-pandemic.
- The focus on API (Active Pharmaceutical ingredients) sourcing and reducing dependence on single regions creates strategic roles for pharmacists with an industrial Pharmacy focus.
Quality Assurance in Pharmacy
Key Roles
The QA Manager oversees the entire Quality Management System (QMS). Their responsibilities include:
- ensuring that every department, like R&D, manufacturing, and Packaging, adheres to documented procedures and regulatory requirements.
- They are also responsible for making the final decision on whether a batch of medicine is fit for release to the market or not.
Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety
Pharmacovigilance is the science and activities that relate to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or any drug-related problem.
The Pharmacist’s Role
- Pharmacists are ideally suited for this role as they understand the drug mechanisms, side effects, and clinical nomenclature.
- They analyse adverse event reports from clinical trials and post-marketing use, ensuring that the risk-benefit profile of the drug remains acceptable.
Industry Demand
- With the increase in global drug surveillance and regulatory reporting requirements, the PV specialist role demand has also increased.
Conclusion
Before choosing pharma career options between clinical and industrial pharmacy, it is important to understand where your interest lies and where you can grow your career.
Both fields are growing, and both are rewarding Pharmacy career options and play an important role in improving health and saving lives.
If you’re interested in patient care and therapeutics, then choose clinical and choose industry if you can get inspired by the innovations.
Ultimately, choose the topic where you can grow and find purpose.




